One key challenge for indirect demand response is properly aligning the interests of participating end-users with grid stakeholders.
Even if this alignment is successful, existing demand response pilots demonstrate that end-user participation must be facilitated through automating measures to achieve sufficient levels of engagement.
Community-level coordination of DERS through a centralized communication architecture has inherent scalability risks.
Concurrently, optimizing on a building-level risks suboptimal reduction of community-level intermittency.
ALEX must combine the best of both and achieve emergent, targeted coordination between selfish participants without explicit communication.
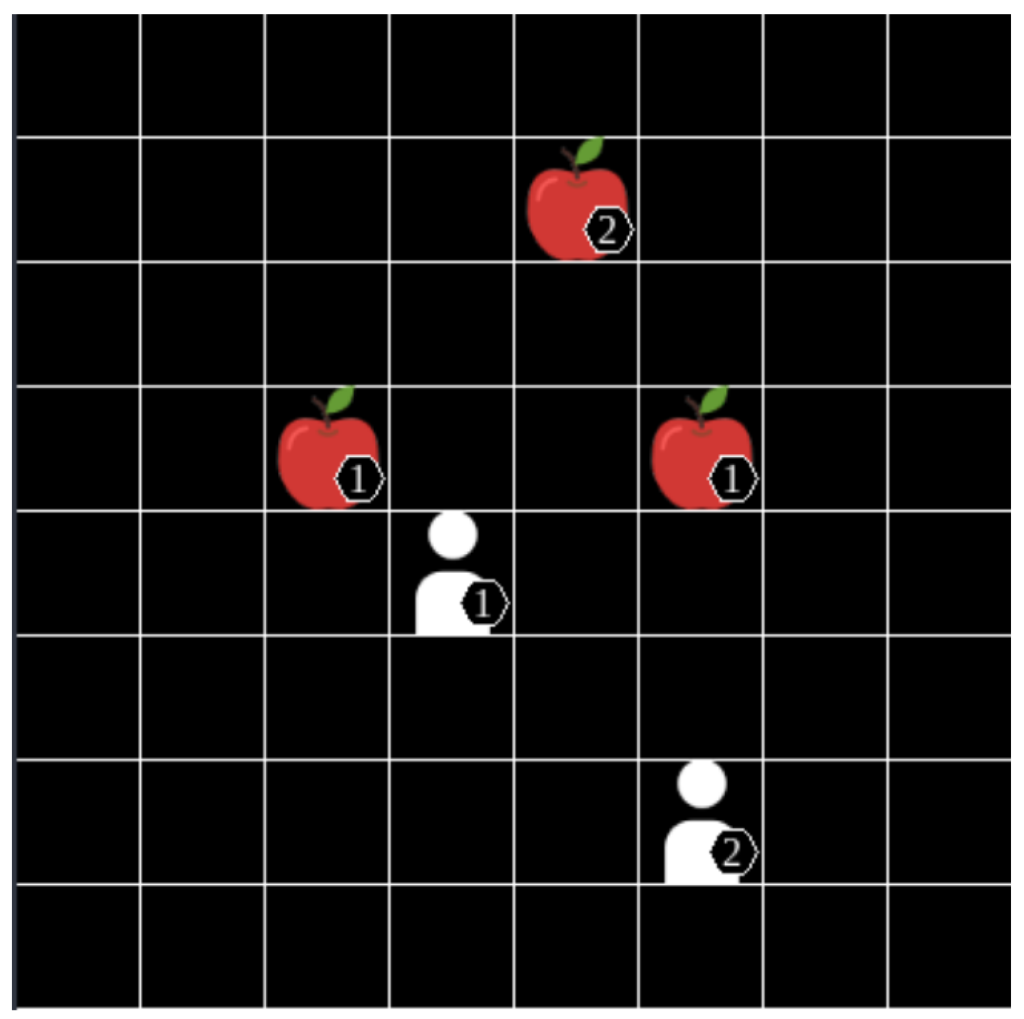
Towards this end, this research explored how the coordination of reinforcement learning agents emerges within sequential social dilemmas.
It delves into the trade-offs of using individual agent reward vs collective team reward and the drawbacks of different training paradigms for multi-agent reinforcement learning settings.
This work concluded that combining an individual reward function with centralized learning decentralized execution algorithms leads to increased agent learning performance for the studied environments.
This informs ALEX’s own RL algorithm design, unlocking one of its key characteristics: community-level coordination of DERs without requiring communication between its selfish participants.
Click here to read the first publication (Investigating Effects of Centralized Learning Decentralized Execution on Team Coordination in the Level Based Foraging Environment as a Sequential Social Dilemma | SpringerLink) or the second publication (Systems | Free Full-Text | It’s All about Reward: Contrasting Joint Rewards and Individual Reward in Centralized Learning Decentralized Execution Algorithms (mdpi.com))
To learn more about how we align grid-stakeholder and end-user interests, look at Steven’s research.